
Research Innovation
FOR LONG COVID PATIENTS
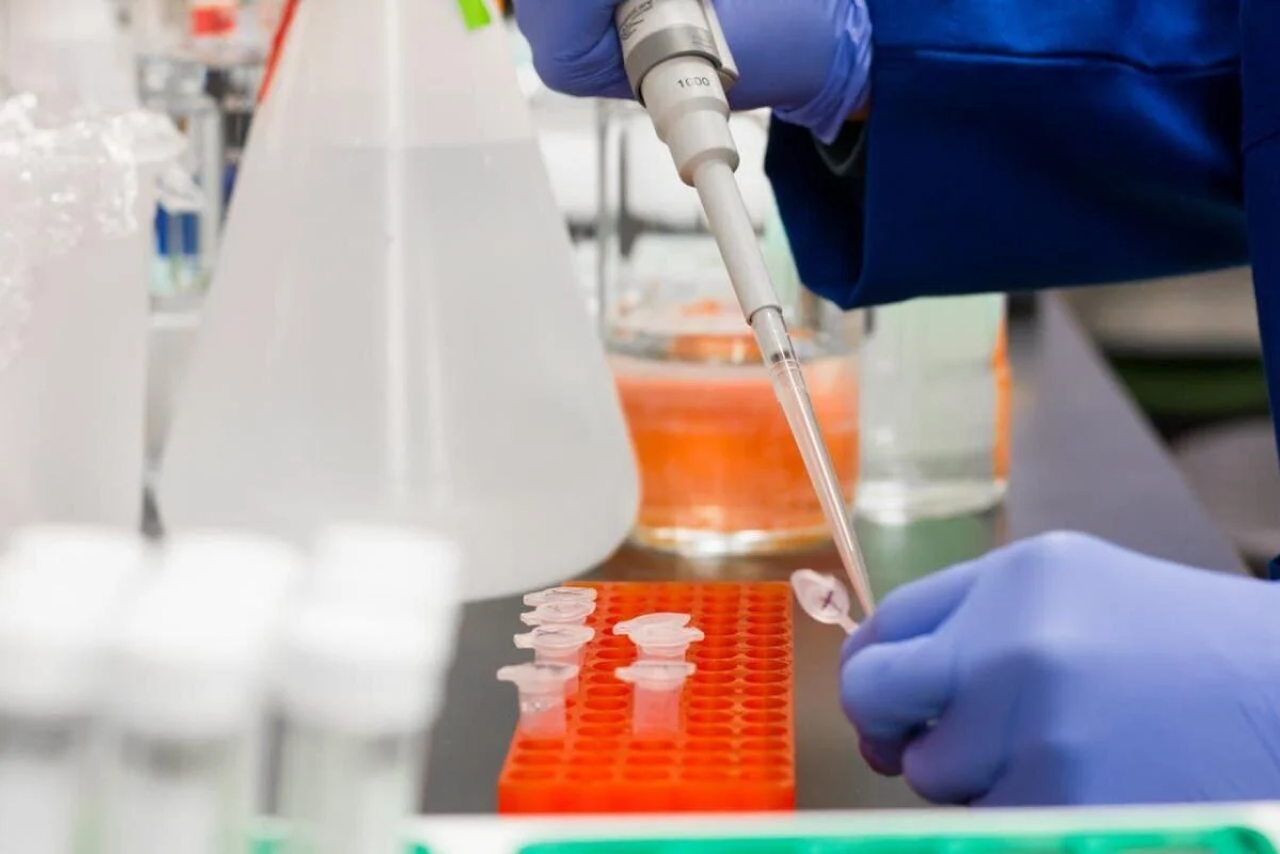
Medical Problem: Diagnosis and Treatment of Long Covid Patients is challenging
Post-acute sequelae of COVID (PASC), commonly referred to as long COVID, is an emerging public health syndrome that continues to devastate and debilitate adult and pediatric survivors of acute SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The World Health Organization (WHO) led Delphi consensus defined PASC as a syndrome starting 3 months from onset of probable infection with symptoms lasting over 2 months and could not be explained by an alternative diagnosis.1
.png?width=505&height=433&name=IMAGE%20(5).png)
Solution:
Determine the root cause of Long Covid symptoms - CCR5 and fractalkine receptors
While conducting HIV research, Dr. Patterson studied the CCR5 immune pathway and tested how it mediates vascular inflammation.
In Long Covid patients, the SI protein of the COVID-19 virus remains in their monocytes, leading to a persistent immune response despite the absence of active COVID-19 infection. These monocytes have many CCR5 and fractalkine receptors on their surface, which promote vascular inflammation and immune dysregulation through the monocytic-endothelial-platelet axis.

RESOURCE ARTICLE
Frontiers in Immunology
Persistent of Sars CoV-2 S1 Protein in CD16+ Monocytea in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) up to 15 Months Post-Infection
IncellKINETM,
RUO diagnostic test
is designed to detect Long Covid immune signature
IncellKINE, is intended to identify patients with Long-Covid. This simple blood test can help to objectively diagnose patients suffering from Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC), commonly known as Long Covid.
The test was developed based on clinical studies published in the peer reviewed journal Frontiers in Immunology, which showed that researchers utilized machine learning and artificial intelligence to measure and analyze sets of inflammatory markers called cytokines and chemokines. The studies also demonstrated that patients with previous COVID-19 infection and lingering symptoms were found to have a distinct immunological profile characterized by patterns of inflammatory marker expression.
In a subsequent publication, it was discovered that SARS CoV-2 S1 spike protein remains in monocytic reservoirs of Long Covid patients up to 15 months after acute infection.

RESOURCE ARTICLE
National Library of Medicine
Immune-Based Prediction of COVID-19 severity and Chronicity Decoded Using Machine Learning
Click to view the 14 cytokines measured in the test:
Click HereS1 Immune Panel Test
The S1 Immune Subset looks for the presence of SARS COV 2-S1 protein in monocytes resulting from either the COVID-19 vaccine or natural infection. This test also includes CD3, CD4 and CD8 % and absolute count in addition to monocyte subset percentage with and without S1 protein in all classical, non-classical, and intermediate monocytes.
The S1 Immune subset confirms if the S1 is in your system and most likely the cause for the long hauler symptoms.
Post-acute sequelae SARS-CoV-2 infection (PASC) is a disabling and sometimes debilitating condition that occurs in 10%-30% of individuals infected by SARS-CoV-2 and has recently been proposed to cause neurologic symptoms in 30% of those infected.

Recently Dr. Patterson and his team identified characteristic immune cell subset abnormalities that accompanied the unique cytokine/chemokine profile.
They also found kinetic differences in the proportions of monocyte subsets in severe cases and PASC, as well as the presence of SARS-CoV-2 protein unaccompanied by corresponding viral RNA in CD14lo, CD16+ monocytes in PASC patients up to 16 months post-acute SARS-CoV-2 infection.
The predominant immune cell abnormality they observed in their work was elevations in monocyte subsets. Monocyte subpopulations are divided into 3 phenotypes, and they are functionally distinct from each other.
CLICK TO VIEW THE 3 MONOCYTES MEASURED IN S1 TEST:
Click HereIdentifying the immune subset population may provide information in understanding symptoms associated with inflammatory phenotype of these senescent nonclassical monocytes and assist in the treatment of PASC.
Maraviroc and Pravastatin in combination:
potential treatment option for Long Covid patients
HealthBio is studying a drug combination to address immune dysregulation in Long Covid and other immune-mediated diseases.
This drug combination of maraviroc (CCR5 antagonist) and pravastatin (fractalkine inhibitor) disrupts the monocytic-endothelial-platelet axis, reducing vascular inflammation and restores immune homeostasis.
This combination therapy of maraviroc
and pravastatin was studied with positive clinical outcomes. This was the catalyst for the application submission to FDA for the 505 (b) (2) clinical trial which was accepted in January, 2024.
RESOURCE ARTICLE
National Library of Medicine
Case Series: Maravioc and Pravastatin as a Therapeutic Option to treat Long Covid/Post-Acute Sequealae of Covid (PASC)
Collaborate With Us
If you are a Medical Professional and would like to be included in ongoing distribution of clinical information or attend a future webinar, please provide us with your contact information.
.png)
1. Soriano J, Murthy S, Marshall J, Relan P, Diaz, Who Clinical Case Definition Working Group on Post-Covid-19 Condition. A clinical case definition of Post-COVID-19 condition by a Delphi consensus. Lancet Infect Dis. (2021) S1473-3099:703-9.
2. Davis H, Assaf G, McCorkell L, Wei H, Low R, Re’em Y, et al. Characterizing long COVID in a international cohort: 7 months of symptoms and their impact. EClinicalMedicine. (2021) 38:101019. doi: 10.1016/j.eclinm.2021.10109
3. Patterson et al, Persistence of SARS CoV-2 S1 Protein in CD16+ Monocytes in Post-Acute Sequelae of COVID-19 (PASC) up to 15 Months Post-Infection, Frontiers in Immunology.12, 2022.
4. Kapellos T et al.,.Human Monocyte Subsets and Phenotypes in Major Chronic Inflammatory Diseases Frontiers in Immunology; 10, 2019
5. Patterson BK, et al. CCR5 Inhibition in CriticalCOVID-19 Patients Decreases Inflammatory Cytokines, Increases CDS T- Cells, and Decreases SARS-CoV2 RNA in Plasma by Day 14. IntiJ Infect Dis 2020
6. Patterson Bruce K., Guevara-Coto Jose, Yogendra Ram, Francisco Edgar B., Long Emily, Pise Amruta, Rodrigues Hallison, Parikh Purvi, Mora Javier, Mora-Rodríguez Rodrigo A.Immune-Based Prediction of COVID-19 Severity and Chronicity Decoded Using Machine Learning Frontiers in Immunology, 12, 2021;2520
7. Patterson BK, et al. CCR5 Inhibition in Critical COVID-19 Patients Decreases Inflammatory Cytokines, Increases CDS T- Cells, and Decreases SARS-CoV2 RNA in Plasma by Day 14. Inti J Infect Dis 2020
8. Patterson BK, et al. Immune-Based Prediction of COVID-19 Severity and Chronicity Decoded Using Machine Learning. BioRxiv 2020
9. Zhang, JM, An J. Cytokines, Inflammation, and Pain. lnt Anesthesia! Clin 2007;45(2):27-37.
10. Sokol, CL, Luster AD. The Chemokine System in Innate Immunity. Cold Spring Harb Perspect Biol2015;7: a016303.
11. CD4+T, CD8+T counts and severe COVID-19: A meta-analysis. Zhang H, Wu T. J Infect. 2020 Sep;81(3): e82-e84.
12. Lymphocyte subset (CD4+, CD8+) counts reflect the severity of infection and predict the clinical outcomes in patients with COVID-19. Liu Z et al., J Infect. 2020 Aug;81(2):318-356.
13. T-Cell Subset Counts in Peripheral Blood Can Be Used as Discriminatory Biomarkers for Diagnosis and Severity Prediction of Coronavirus Disease 2019. Jiang M, Guo et al., J Infect Dis. 2020 Jun 29;222(2):198-202.

